Wound closure is a crucial aspect of healthcare that requires precision and attention to detail. Healthcare professionals, regardless of their specialties, must know how to treat different types of wounds and ensure patients get the best possible care. There are several techniques and tools available to minimize complications and ensure proper healing. With this step-by-step guide to wound closure, we will outline the different techniques and tools used by healthcare professionals and explain what makes them so important.
Step One: Preparation
Before starting the wound closure process, a medical professional must prepare the patient and the wound site. The patient should rest in a comfortable and accessible manner that still allows the provided to work without trouble. They must clean the wound thoroughly and remove all foreign materials prior to starting the closure process. If necessary, the provider or members of their team will get all the necessary materials and tools ready, including local anesthesia, sterilized equipment, and sutures. Quality surgical needles and holders are especially important for this process as they provide the most control when performing suturing techniques.
Step Two: Anesthesia
Local anesthesia works to alleviate pain and discomfort during the procedure. The healthcare professional should administer the anesthesia by injecting it into the wound site or the surrounding area, depending on the location and severity of the wound. They will allow the anesthesia some time to take effect before proceeding with the closure process.
Step Three: Closure Techniques
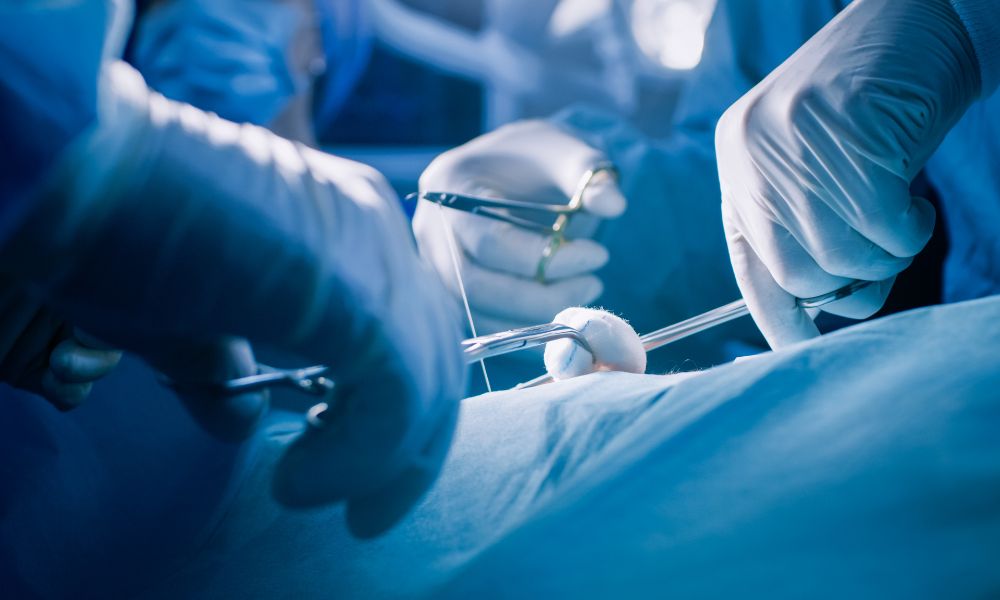
Once the patient is fully prepared for treatment, the next step in this guide to wound closure is for the medical provider to decide on a specific suture method. There are different techniques for wound closure, depending on the type and location of the wound. Sutures, staples, and tissue adhesives are the most common methods used by healthcare professionals. Sutures involve the use of a needle and thread to close the wound by stitching it together. Staples are metallic clips that close the wound by holding the edges together. Tissue adhesives, also known as skin glue, use a special type of glue to bond the wound edges.
Step Four: Suture Techniques
Sutures are the most commonly used method for wound closure, and there are different techniques to ensure proper healing and minimize scarring. Interrupted sutures use a needle to make individual stitches along the wound, while continuous sutures involve a longer thread that runs continuously across the wound. Subcuticular sutures weave beneath the skin to minimize scarring and reduce the risk of infection. The choice of suture technique depends on the location and type of wound.
Step Five: Post-Closure Care
After closing the wound, the healthcare professional must provide proper post-care instructions for the patient. This includes guidelines for cleaning the wound regularly, keeping it dry, and avoiding activities that may compromise the healing process. The provider should monitor the wound for any signs of infection or other complications and make necessary adjustments to the post-care plan if needed.
Wound closure is an essential skill for any healthcare professional, and mastering the various techniques is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications. By following these guidelines, providers can ensure successful wound closure every time.






